Research Progress
Research Progress
- Oxidation-responsive OEGylated poly-L-cysteine and solution properties studies
- Effects of the surface charge on the stability of PEG-b-PCL micelles: simulation of the interactions between charged micelles and plasma components
- Supramolecular Hydrogels Assembled from Nonionic Poly(ethylene glycol)-b-Polypeptide Diblock Containing OEGylated Poly-L-glutamate
- Surface-Induced Hydrogelation Inhibits Platelet Aggregation
- Stimuli-responsive polypeptide materials prepared by ring-opening polymerization of α-amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides
- Effects of molecular weight on thermal responsive property of PEGylated poly-L-glutamates
- Facile Synthesis of Dendrimers Combining aza-Michael Addition with Thiol-yne Click Chemistry
- Peptide Hydrogels Assembled from Nonionic Alkyl-polypeptide Amphiphiles Prepared by Ring-Opening Polymerization
- SYNTHESIS OF TOOTHBRUSH COPOLYPEPTIDES BASED ON POLYLYSINE BACKBONE
- One-step synthesis of water dispersible silica nanoplates
- Conformation-specific Self-assembly of Thermo-responsive Poly(ethylene glycol)-b-polypeptide Diblock Copolymer
- Coassembly of Poly(ethylene glycol)-block-Poly(glutamate sodium) and Gemini Surfactants with Different Spacer Lengths
- Thermoresponsive Oligo(ethylene glycol) Functionalized Poly‑L‑cysteine
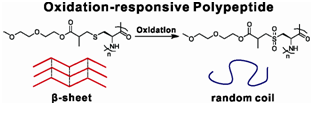
 Oxidation-responsiveOEGylated poly-L-cysteine and solution properties studies
Oxidation-responsiveOEGylated poly-L-cysteine and solution properties studies
Oxidation-responsiveOEGylated poly-L-cysteine and solution properties studies
Biomacromolecules, 2014, 15, 1055-1061
Xiaohui Fu, Yinan Ma,Yong Shen, Wenxin Fu and Zhibo Li*
The oxidation-responsive behaviors of OEGylated poly-L-cysteine homopolypeptides, i.e., poly(L-EGxMA-C)n, were investigated. These poly-L-cysteine derivatives adopted mixed conformationin water, in whichtheβ-sheet accounted for a significant proportion. Upon oxidation, the thioethers in polypeptide side-chains were converted to polar sulfone groups, which triggered the secondary structure transition from β-sheet preferred conformation to random coil. Accordingly, the increase of side-chain polarity together with conformation changes increased samples' water solubility and cloud pointtemperature. Using mPEG45-NH2 as macroinitiator, we synthesized PEG45-b-poly(L-EG2MA-C)22 diblock copolymer via ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of L-EG2MA-C N-carboxyanhydride (NCA). The PEG45-b-poly(L-EG2MA-C)22 was able to self-assemble into spherical micelles in aqueous solution, and the micelles could undergo an oxidation-triggered disassembly due to the oxidation-responsive thioethers. Such new class of oxidation-responsive polypeptides might provide a promising platform to construct inflammation targeting drug delivery systems.